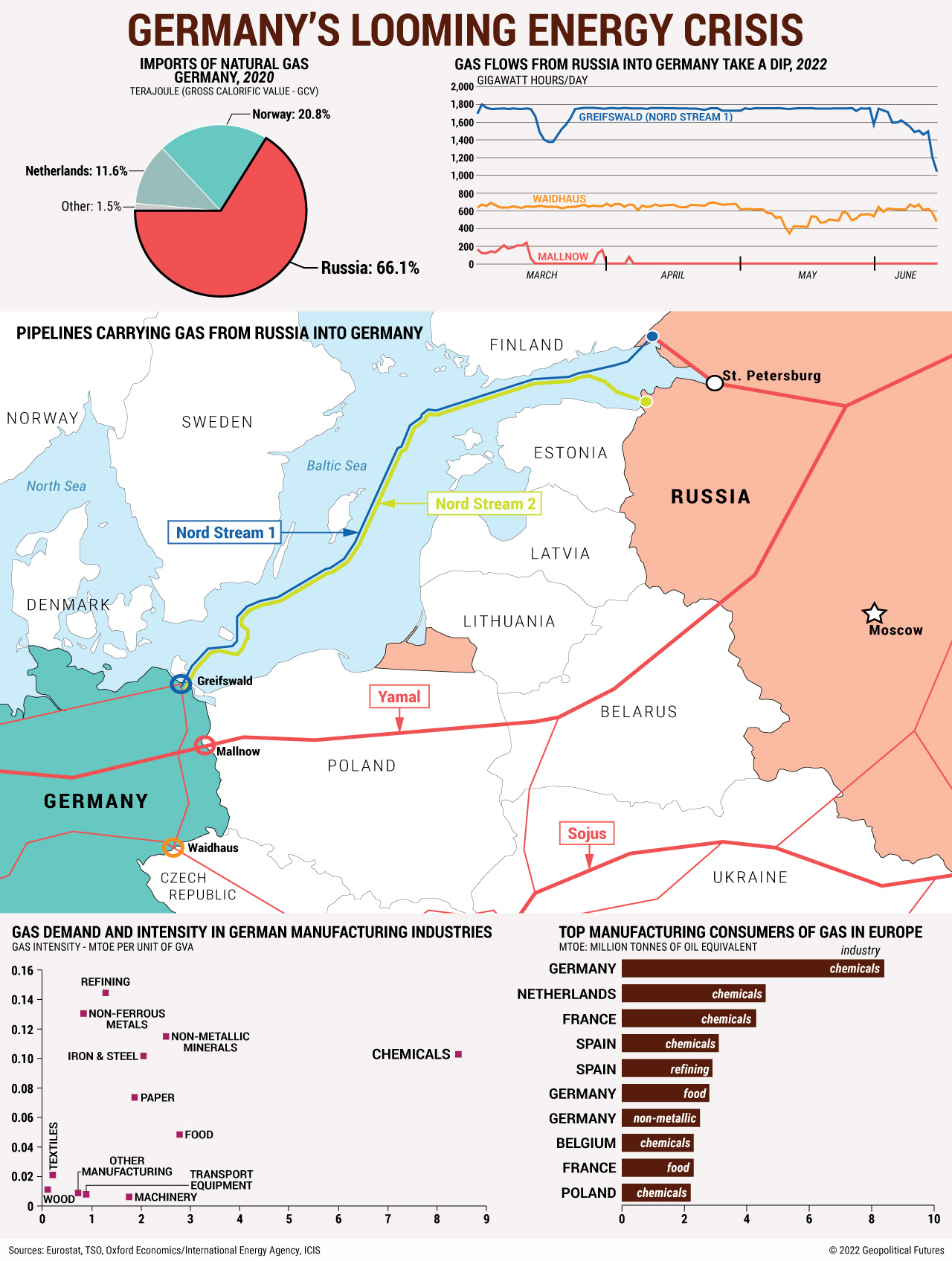
Germany, Europe’s economic powerhouse, is one of the largest economies in the world. German industrial firms, however, are increasingly facing production problems. Among the causes are logistical issues arising from the crisis in Ukraine and COVID-19 containment measures. But the biggest driver is the energy crisis, in part a result of Germany’s dependence on cheap Russian natural gas, which is now severely restricted.
The most important sectors of the German economy, many of which are energy-intensive industries such as the chemical sector, have seen rising production costs due to high gas and electricity prices. Some have even closed operations, reduced production or plan to transfer certain operations to North Africa or Southeast Asia. This could lead to job cuts in Germany, slowing economic growth and declining exports. To stave off these effects, Germany will have to increase subsidies for the affected industries, find ways to use energy more efficiently, find new sources of energy or make compromises with Moscow. It’ll be a difficult choice for Berlin but, as winter approaches, one it can’t avoid.




 Special Collection – The Middle East
Special Collection – The Middle East